Zinc and hormonal balance go hand in hand, making zinc essential for maintaining endocrine health in today’s stressful world. This essential trace mineral isn’t just a buzzword in multivitamins—it’s a fundamental player in the symphony of hormones that regulate everything from metabolism and mood to reproduction and stress response. Zinc deficiency affects over a billion people globally, often silently undermining hormonal health until symptoms like fatigue, irregular cycles, or low libido emerge.
But why does zinc matter so much to our endocrine system? At its core, zinc acts as a cofactor for hundreds of enzymes, a structural component in proteins, and a regulator of gene expression. In the context of hormones, it influences synthesis, metabolism, receptor binding, and even cellular signaling. From the adrenal glands pumping out adrenaline during a deadline crunch to the thyroid orchestrating your daily energy, zinc is the quiet conductor ensuring everything runs smoothly. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into zinc’s relationships with key hormones—adrenaline, progesterone, thyroid hormones, testosterone, estrogen, and DHEA—while exploring signs of deficiency and practical tips for optimization. By the end, you’ll see why prioritizing zinc could be the missing piece in your hormonal puzzle.
Zinc and Adrenaline: Navigating the Stress-Zinc Tug-of-War with Hormonal Balance
Chronic stress is a modern epidemic, and at its heart lies adrenaline, the “fight or flight” hormone that surges through your veins during high-pressure moments. While a quick adrenaline hit can sharpen focus and mobilize energy, excess and persistent elevation—as seen in ongoing anxiety, work overload, or trauma—takes a toll on your body’s zinc reserves. Research consistently shows that prolonged catecholamine spikes, like those from adrenaline and noradrenaline, lead to zinc depletion over time. This isn’t just theoretical; human and animal studies reveal reduced zinc absorption in the gut, heightened urinary excretion, and mobilization from vital stores without proper replenishment.
The mechanism is fascinating yet concerning. Acutely, a single adrenaline surge might cause a transient redistribution of zinc, temporarily boosting levels in tissues like red blood cells and the liver for immediate survival needs. Think of it as your body borrowing from its zinc bank to fuel the stress response—enhancing immune readiness or repairing minor damages on the fly. However, when stress becomes chronic, these adaptive tricks falter. The gut’s zinc transporters get overwhelmed, leading to malabsorption, while kidneys flush out more zinc to cope with the inflammatory load. Over weeks or months, this results in lower total body zinc, impairing everything from immune function to cognitive clarity.
The ripple effects are profound. Zinc-depleted individuals under chronic stress often experience amplified symptoms: weakened immunity leading to frequent infections, foggy thinking, and even delayed wound healing. Nutritional research underscores that this depletion can create a vicious cycle, where low zinc exacerbates stress sensitivity, further elevating adrenaline. Clinically, this manifests in conditions like adrenal fatigue or burnout, where patients report exhaustion despite adequate sleep. To break the loop, monitoring zinc status through blood tests or symptoms is key, especially for high-stress professions like healthcare workers or executives.
Fortunately, intervention is straightforward. Zinc supplementation, paired with stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness or exercise, can restore balance. Studies show that correcting zinc levels not only curbs adrenaline’s depleting effects but also enhances resilience to future stressors. Foods rich in zinc—oysters, pumpkin seeds, and beef—offer a natural buffer, but for those with absorption issues, chelated forms like zinc picolinate may be more effective. In essence, respecting the adrenaline-zinc dynamic isn’t just about surviving stress; it’s about thriving beyond it.
Zinc and Progesterone: Guardians of Reproductive Harmony
Progesterone, the hormone of pregnancy and calm, dances a delicate tango with zinc and hormonal balance, particularly in women’s reproductive cycles. Zinc isn’t merely supportive—it’s indispensable for progesterone’s very creation and action. From the ovaries releasing eggs to the uterus preparing for implantation, zinc ensures hormonal precision. Deficiencies here can spell trouble, from irregular periods to fertility challenges, highlighting zinc’s role as a reproductive linchpin.
At the synthesis level, zinc fuels the pituitary gland’s production of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which trigger ovulation and the subsequent progesterone surge in the luteal phase. Without sufficient zinc, these signals weaken, leading to lower progesterone output and symptoms like premenstrual syndrome (PMS) or luteal phase defects. Clinical data links adequate zinc intake to regular cycles and elevated progesterone levels, while deficiency correlates with menstrual chaos—think painful cramps, spotting, or anovulation. Animal models reinforce this: zinc-starved subjects show disrupted ovarian function, underscoring the mineral’s direct hand in steroidogenesis.
Beyond production, zinc fine-tunes progesterone’s effectiveness at the cellular level. It modulates receptor affinity in tissues like the endometrium, enhancing binding at optimal concentrations. This interaction involves zinc’s affinity for sulfhydryl groups on receptors, stabilizing the hormone-receptor complex for better signaling. Intriguingly, progesterone itself may regulate zinc transporters, creating a bidirectional loop that maintains intracellular zinc homeostasis. Disrupt this—through diet, stress, or illness—and you risk diminished tissue responsiveness, exacerbating issues like endometriosis or menopausal hot flashes.
For women navigating hormonal shifts, zinc’s progesterone partnership offers actionable insights. During perimenopause, when progesterone dips, zinc supplementation can stabilize receptors, easing symptoms like mood swings or sleep disturbances. Fertility-focused individuals might prioritize zinc-rich diets to boost oocyte quality and implantation success. Research from nutritional endocrinology suggests 15-30 mg daily for women of reproductive age, but always under guidance to avoid excess, which could paradoxically inhibit binding. Ultimately, honoring this zinc-progesterone alliance empowers women to reclaim cycle sovereignty and reproductive vitality.
Zinc and Thyroid Hormones: The Metabolic Maestro
Your thyroid, that butterfly-shaped gland in your neck, dictates your metabolic rhythm, and zinc is its steadfast ally. From synthesizing thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to converting inactive T4 into potent T3, zinc orchestrates every step. Deficiency doesn’t just slow your engine—it can mimic hypothyroidism, sapping energy and fogging focus, a silent saboteur in an already overworked world.
Zinc’s involvement starts upstream in the brain: it’s vital for thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) production in the hypothalamus, which cues the pituitary to release TSH. Without it, this axis falters, leading to secondary hypothyroidism. Downstream, zinc serves as a cofactor for deiodinase enzymes, the alchemists that activate T4 into T3—the form your cells crave for energy production. Zinc also shapes thyroid nuclear receptors and transcription factors like TTF-2, a zinc-finger protein that flips genetic switches for hormone synthesis. In zinc-poor states, these proteins misfire, reducing hormone output and tissue sensitivity.
The fallout is systemic. Low zinc correlates with depressed T3 and TSH levels, a sluggish basal metabolic rate, and symptoms like unexplained weight gain, cold intolerance, or brittle hair. Human trials show supplementation restores these metrics in deficient individuals, particularly in regions with marginal zinc intake like parts of Asia and Africa. Animal studies echo this: zinc-deprived rodents exhibit thyroid atrophy and impaired gene expression, mirroring human subclinical hypothyroidism.
Clinically, zinc’s thyroid ties extend to autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s, where inflammation further depletes the mineral. Pairing zinc with selenium—another thyroid cofactor—amplifies benefits, as seen in studies on goiter prevention. For optimal health, aim for zinc sources like chickpeas or cashews, and consider testing if fatigue lingers despite lifestyle tweaks. By bolstering this zinc-thyroid bond, you not only rev your metabolism but also safeguard against the cascade of endocrine disruptions that follow.
Zinc and Testosterone: Fueling Male Vitality and Beyond
Testosterone, the emblem of male vigor, owes much to zinc—from its testicular birthplace to its muscle-building prowess. In men, zinc concentrates in the prostate and Leydig cells, where it sparks testosterone synthesis and wards off decline. But its influence isn’t gender-exclusive; everyone benefits from this mineral’s androgenic support, making zinc a unisex hormone hacker.
Mechanistically, zinc stimulates LH release, which prods Leydig cells into testosterone production. It also exerts direct effects, bypassing hormones to amp up steroidogenic enzymes. Deficiency hits hard: serum testosterone plummets, ushering in low libido, erectile woes, muscle loss, and fertility dips like poor sperm motility. Studies on wrestlers and elderly men show dramatic rebounds with zinc repletion—testosterone normalizing in weeks, vitality surging.
Women, too, rely on zinc for hormonal and androgen balance, as testosterone precursors feed into estrogen pathways. Low zinc can skew this, contributing to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) symptoms. Across genders, zinc’s anti-aromatase action curbs excess conversion to estrogen, preserving masculine traits without overkill.
Athletes and aging populations stand to gain most. Zinc curbs exercise-induced drops in testosterone, while in seniors, it counters andropause. Dose wisely—15-50 mg daily—and pair with magnesium for synergy. Foods like lean meats or lentils deliver steady supply. Embracing zinc’s testosterone torch not only reignites drive but fortifies resilience against age’s hormonal theft.
Zinc and Estrogen: Empowering Feminine Equilibrium
Estrogen, the architect of feminine curves and cycles, partners with zinc in a symphony of synthesis and sensitivity. Zinc bolsters FSH and LH for follicular estrogen peaks, while modulating receptors to temper fluctuations. Deficiency disrupts this, inviting menstrual mayhem or menopausal malaise.
At the molecular helm, zinc stabilizes estrogen receptors, enhancing DNA binding for gene regulation in bones, breasts, and brain. It influences transporters like ZnT7, fine-tuning steroid metabolism. Low zinc spikes aromatization—testosterone morphing into excess estrogen—fueling conditions like fibroids or breast tenderness.
Menopause amplifies the stakes: zinc mitigates hot flashes by steadying receptors, supporting bone and skin via estrogen echoes. PMS sufferers find relief too, as zinc curbs cramps and mood dips. Bidirectional ties shine—estrogen tweaks zinc genes, a feedback loop for balance. For deeper insights on zinc’s role in women’s hormonal health, explore how it supports cycle regulation.
For hormonal harmony, zinc shines in perimenopause protocols, often with vitamin D. Women with absorption hurdles (e.g., gut issues) may need supplements. Harnessing this duo transforms estrogen from foe to friend, fostering cycles of strength and serenity.
Zinc and DHEA: Adrenal Architects of Youthful Hormones
DHEA, the adrenal “youth hormone” precursor to sex steroids, leans on zinc for its biosynthetic backbone. Zinc powers enzymes in adrenal cortex cells, ensuring DHEA flows into testosterone and estrogen pipelines. Deficiency mutes this, tilting hormone ratios toward imbalance.
Zinc fingers like SF1 orchestrate DHEA enzyme genes, while transporters maintain cellular zinc for catalysis. Low levels ripple to androgens/estrogens, impacting energy, libido, and immunity. Stress exacerbates, as adrenal demand outstrips zinc supply.
Clinically, zinc aids DHEA in anti-aging and metabolic health, countering inflammation. Supplementation in deficient elders boosts DHEA metabolites, easing fatigue. Adrenal-support diets—nuts, seeds—sustain this. Zinc’s DHEA dance preserves hormonal youth, warding off decline’s shadow.
Spotting Zinc Deficiency: Beyond the Hormonal Balance
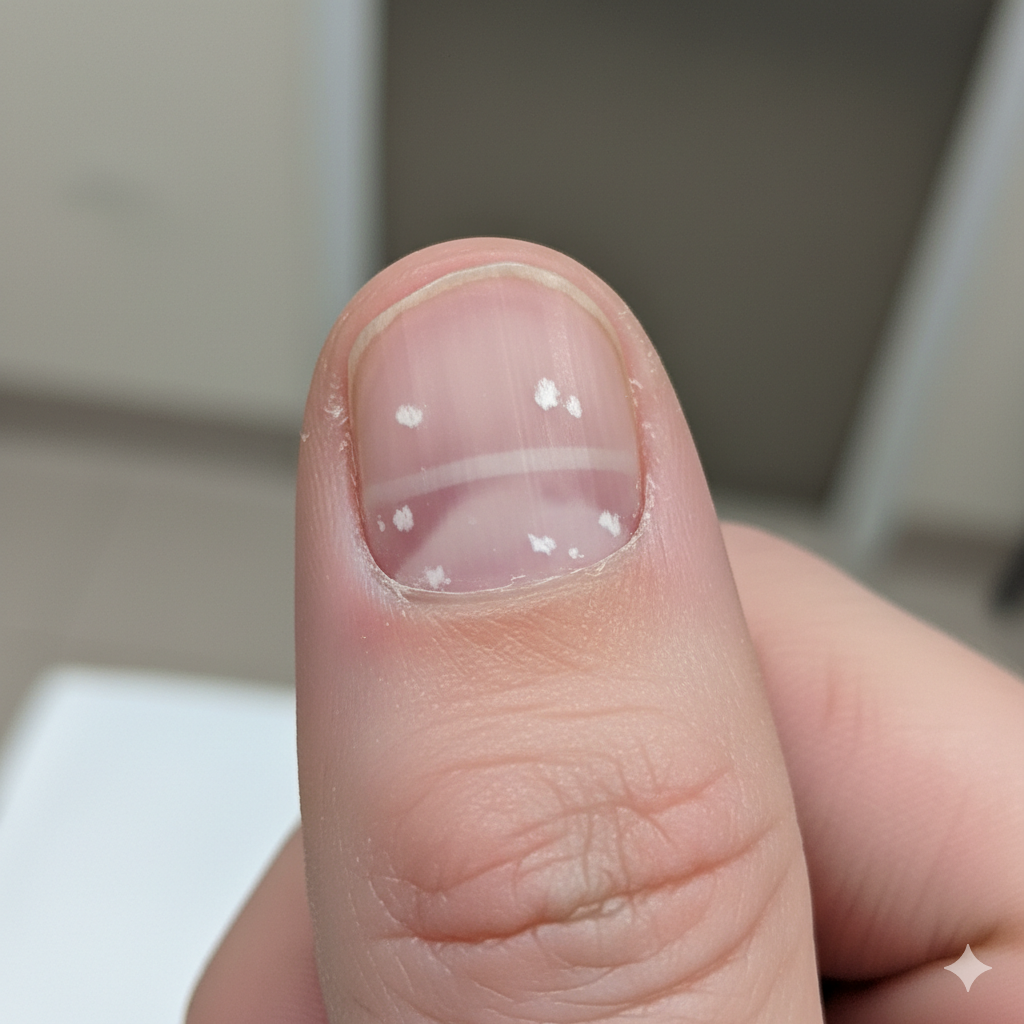
Zinc shortfall sneaks up, but clues abound. Beyond low alkaline phosphatase (ALP)—a zinc-reliant enzyme dipping in deficiency—watch for infections, slow healing, hair loss, or taste loss. ALP’s sensitivity shines, but confounders like hypothyroidism muddy it; pair with serum zinc for clarity.
Nail telltales like white spots (leukonychia) flag issues, tied to keratin glitches, though trauma mimics. GI woes, irritability, or growth stalls in kids round out the roster. Holistic assessment trumps single markers.
Conclusion: Reclaim Your Zinc-Powered Endocrine Edge and Restore Hormonal Balance
Zinc’s endocrine web—from adrenaline’s brake to DHEA’s spark—underpins vitality. Deficiency’s toll is steep, but awareness arms you. Test, supplement smartly, eat zinc-forward. Your hormones will thank you with balanced bliss. Consult pros, but start today—your inner alchemist awaits.
Featured Products
Discover more from The Wellness By Design Project
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

